How Are The Price And Demand For Changes In Real Estate Prices Related
four.ane Housing Supply and Demand
Learning Objectives
Afterward you have read this section, you should be able to answer the following questions:
- What factors underlie the demand for housing?
- What factors underlie the supply of housing?
- What determines the amount of housing traded and the price of housing?
The first two articles nosotros quoted from made it clear that the housing market was heavily affected by the fiscal crisis. More than than that, information technology was where the crunch began—and and so it is where we begin our story.
We commencement with the marketplace for new homes, which are role of real gdp (existent GDP). (The ownership and selling of existing homes is not counted in Gross domestic product.) New homes are supplied by construction firms and demanded by families wishing to live in a new domicile. New homes are as well bought past speculators who purchase houses in the promise that they tin resell them for a college toll in the time to come.
Toolkit: Department 16.half-dozen "Supply and Need"
Supply and demandA framework that explains and predicts the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity of a good. is a framework we apply to explain and predict the equilibrium price and quantity of a skilful. A point on the market supply bend shows the quantity that suppliers are willing to sell for a given price. A point on the market need curve shows the quantity that demanders are willing to purchase for a given cost. The intersection of supply and demand determines the equilibrium price and quantity that will prevail in the market.
The toolkit contains a presentation of supply and need that you tin can use for reference purposes in this and the following chapters.
The supply-and-demand framework applies to the case that economists phone call a competitive marketplaceA market that satisfies two weather condition: (1) there are many buyers and sellers, and (two) the goods the sellers produce are perfect substitutes. . A market is said to be competitive, or, more precisely, to exhibit perfect contest, under two weather condition:
- In that location are many buyers and many sellers, all of whom are small relative to the marketplace.
- The goods that sellers produce are perfect substitutes.
In a competitive market, buyers and sellers have the price every bit given; they think their actions have no upshot on the toll in the market place.
Demand
The market demand for housing is shown in Figure 4.i "The Market place Demand for Houses". We call this the market place demand curveThe number of units of a good or a service demanded at each price. because it reflects the choices of the many households in the economy. In macroeconomics, we typically wait at markets at this level of aggregation and do not worry much about the individual decisions that underlie curves such as this one.
Effigy 4.ane The Market Demand for Houses
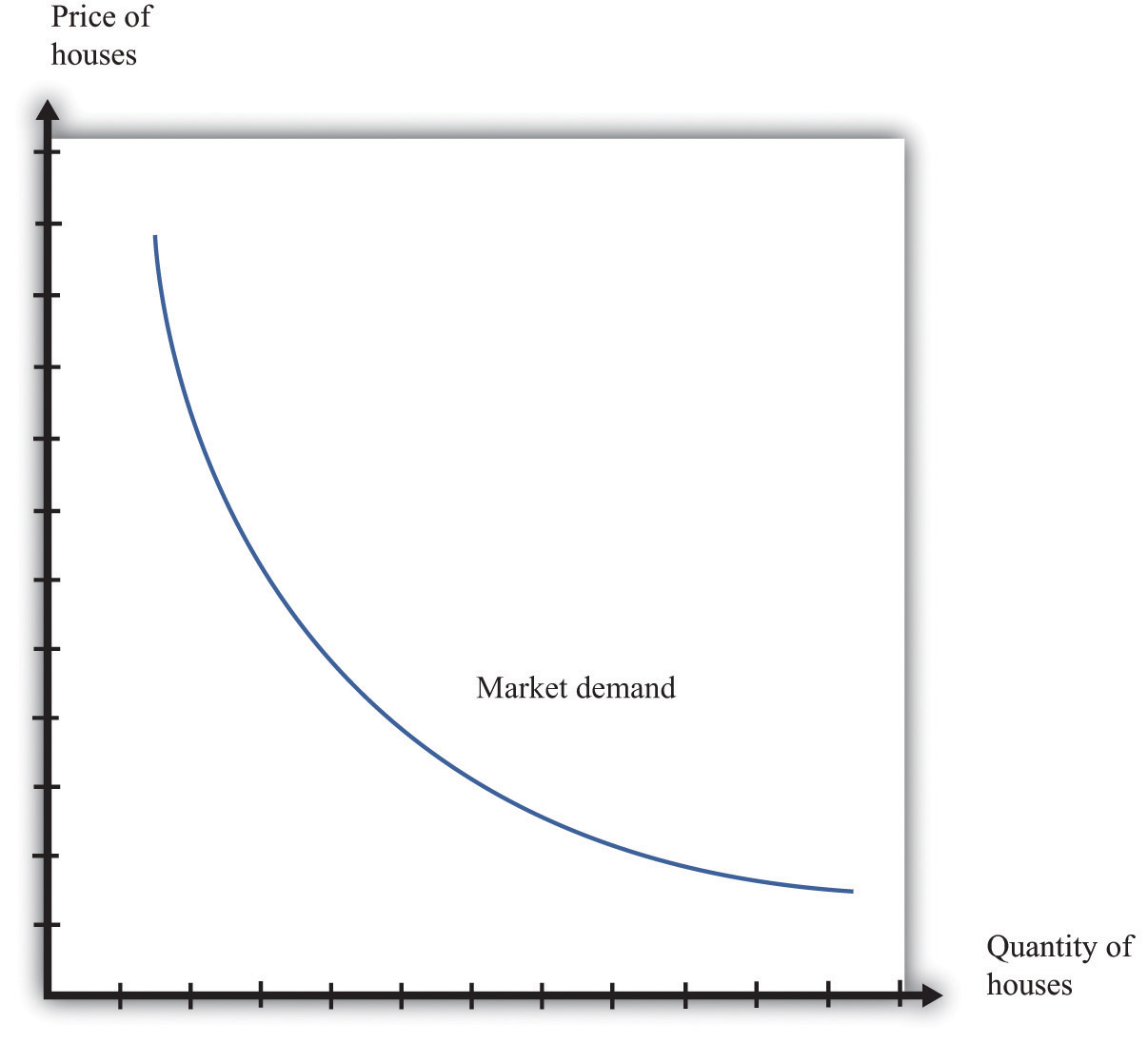
The market demand curve shows the quantity of houses demanded at each price.
Every bit the price of housing decreases, the quantity demanded increases. This is an example of the constabulary of demand, which derives from two furnishings:
- Every bit the price of a good or service decreases, more individuals choose to buy a positive quantity rather than zippo.
- As the price of a good or a service decreases, individuals cull to purchase a larger quantity.
In the case of the market for housing, the commencement of these is more important. Virtually people own either zero houses or one house. As houses become cheaper, more than people decide that they tin can afford a house, so the quantity demanded increases. A few people might decide to buy an additional firm, just they would presumably be in the rich minority. For other goods, such every bit chocolate bars or shoeshines, the second issue is more of import: every bit cost decreases, people increase the quantity that they buy.
Shifts in Demand
When we describe a demand curve, we are varying the price but belongings everything else fixed. In particular, nosotros hold fixed the level of income, the prices of other appurtenances and services in the economy, and the tastes of households. If these other factors change, and so the market demand curve will shift—that is, the quantity demanded will change at each price.
A leftward shift of the market demand bend for houses, as indicated in Effigy iv.2 "A Shift in the Market Demand Curve", could be caused by many factors, including the following:
- A decrease in the incomes of households in the market
- Concerns about the future wellness of the economic system
- A reduction in the price of a typical apartment rental
- An increment in the interest rates for mortgages
- A alter in social tastes so that ownership a business firm is no longer viewed equally a status symbol
Figure iv.ii A Shift in the Market Demand Curve
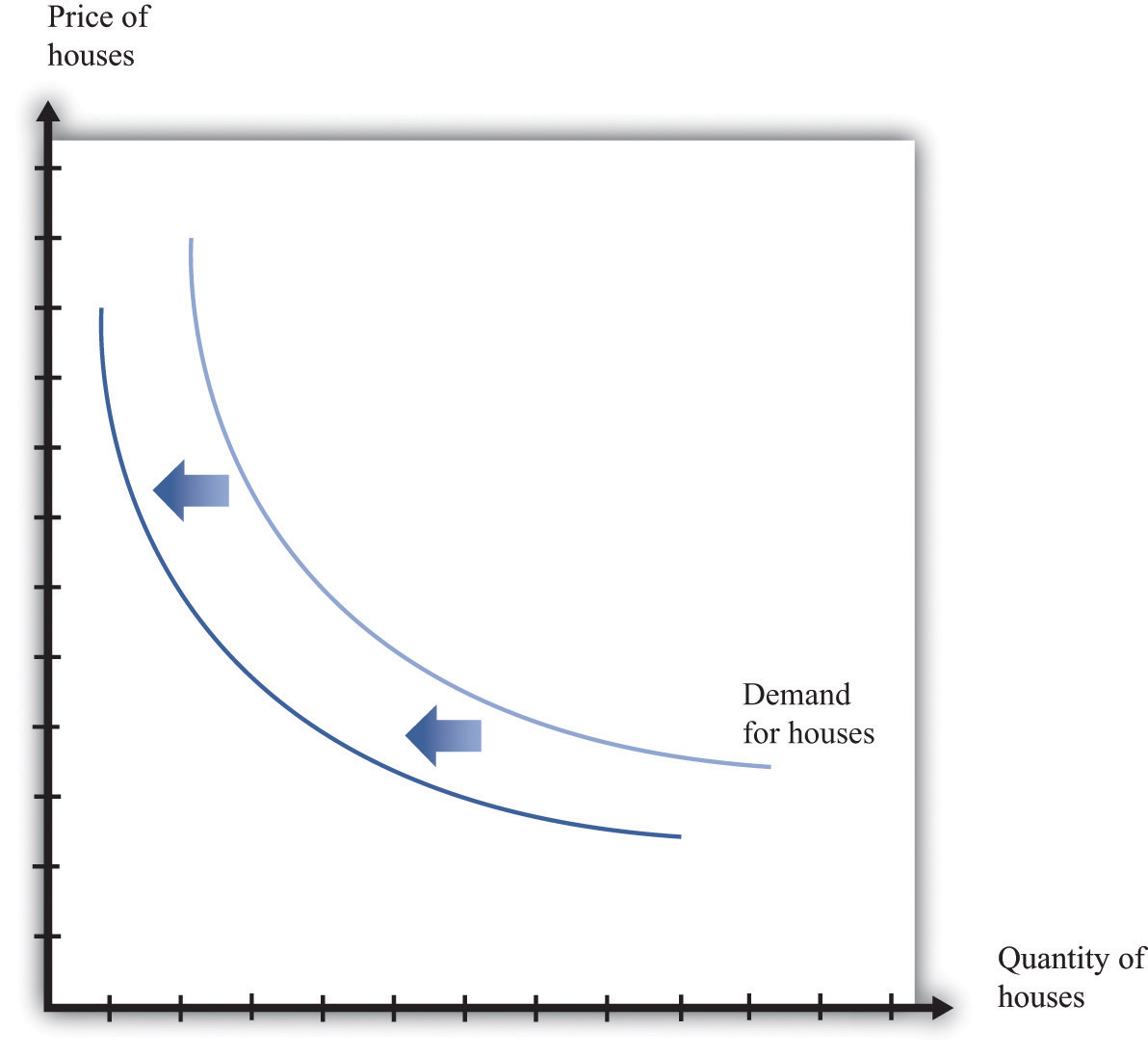
If there is a subtract in need for houses, then fewer houses are demanded at each price. The demand bend shifts leftward.
Supply
The counterpart to the market demand curve is the marketplace supply curveThe number of units of a good or a service supplied at each cost. , which is obtained by adding together the individual supply curves in the economy. The supply curve slopes upwards: as cost increases, the quantity supplied to the market increases. As with demand, there are two underlying effects.
- As price increases, more firms decide to enter the market—that is, these firms produce some positive quantity rather than zero.
- As price increases, firms increase the quantity that they wish to produce.
Figure 4.three The Market Supply of Houses
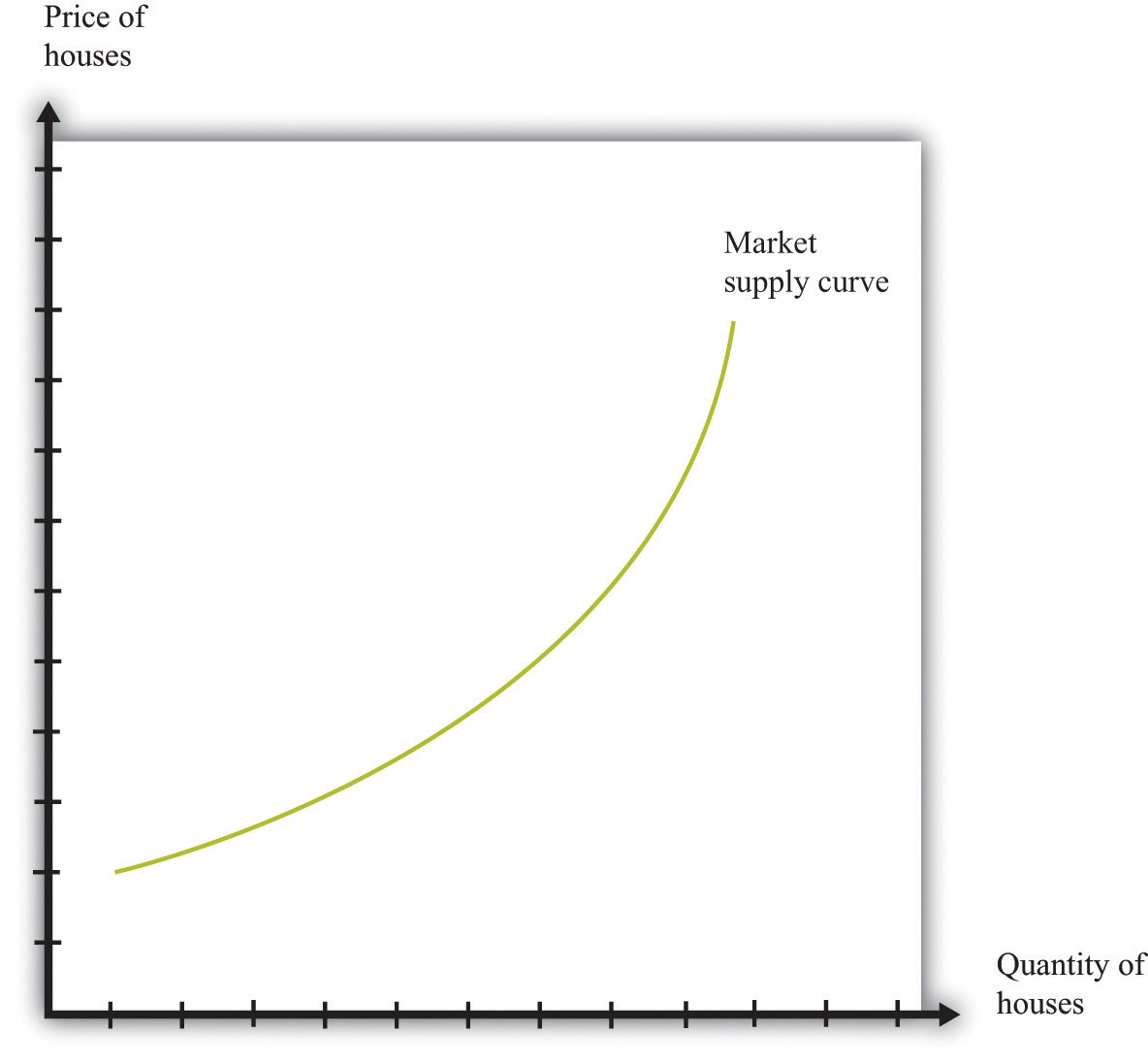
The market supply curve shows the quantity of houses supplied at each price. It has a positive gradient: every bit the price of houses increases, the number of houses supplied to the market place increases likewise.
Shifts in Supply
When nosotros draw a supply curve, we again vary the price but hold everything else fixed. A change in any other factor will cause the market supply curve to shift. A leftward shift of the market place supply bend for houses, equally indicated in Figure 4.four "A Shift in Supply of Houses", could exist caused past many factors, including the following:
- Increases in the costs of production, such every bit wages, the cost of borrowing, or the price of oil
- Bad weather that delays or damages construction in procedure
- Changes in regulations that make it harder to build
Figure 4.4 A Shift in Supply of Houses
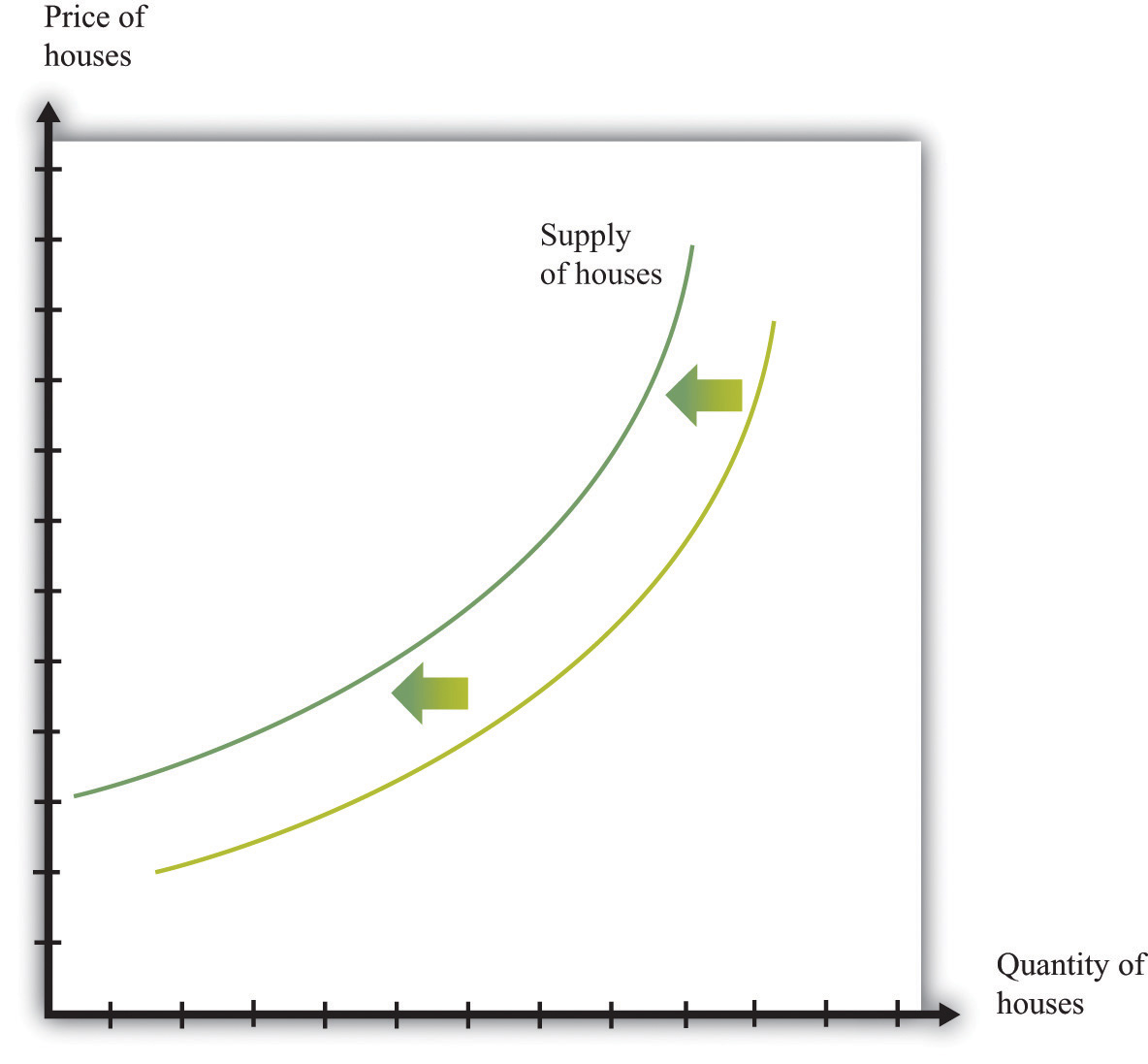
If at that place is a decrease in supply of houses, then fewer houses are supplied at each toll. The supply bend shifts leftward.
Marketplace Equilibrium: What Determines the Price of Housing?
We now put the market need and market place supply curves together to give united states the supply-and-need film in Figure four.5 "Market Equilibrium". The point where supply and need meet is the equilibrium in the market place. At this point, at that place is a perfect lucifer betwixt the amount that buyers want to buy and the amount that sellers want to sell.
Toolkit: Department 16.vi "Supply and Demand"
Equilibrium in a market refers to an equilibrium cost and an equilibrium quantity and has the following features:
- Given the equilibrium price, sellers supply the equilibrium quantity.
- Given the equilibrium price, buyers demand the equilibrium quantity.
Figure 4.v Market Equilibrium
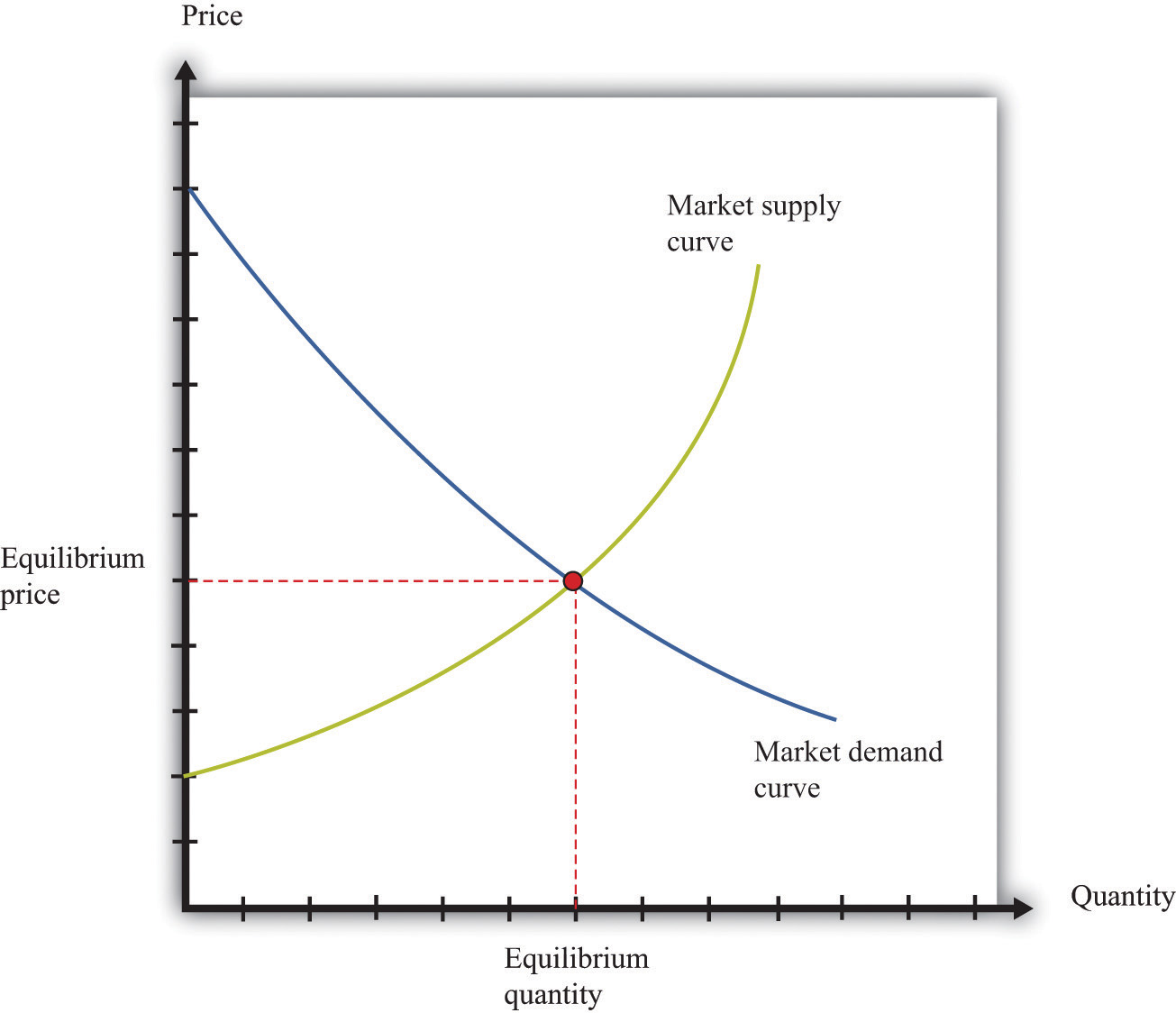
In a competitive market, equilibrium price and quantity are determined past the intersection of the supply and demand curves.
We speak of equilibrium considering there is a balancing of the forces of supply and demand in the market place. At the equilibrium tollA toll such that the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded. , suppliers of the good can sell equally much as they wish, and demanders of the good tin buy every bit much of the good equally they wish. There are no disappointed buyers or sellers. Because the demand bend has a negative slope and the supply curve has a positive slope, supply and demand will cross once, and both equilibrium toll and equilibrium quantityThe quantity supplied and demanded at the equilibrium price. will exist positive.
Table iv.one "Market Equilibrium: An Instance" provides an example of market equilibrium. It gives marketplace supply and marketplace demand for four different prices. Equilibrium occurs at a price of $100,000 and a quantity of 50 new houses.
Table 4.1 Market Equilibrium: An Instance
| Cost ($) | Market Supply | Market Need |
|---|---|---|
| ten,000 | 5 | 95 |
| fifty,000 | 25 | 75 |
| 100,000 | 50 | 50 |
| 200,000 | 100 | 0 |
Economists typically believe that a perfectly competitive market is likely to reach equilibrium. The reasons for this belief are as follows:
- If price is different from the equilibrium cost, then there volition be an imbalance between need and supply. This gives buyers and sellers an incentive to behave differently. For example, if price is less than the equilibrium price, demand will exceed supply. Disappointed buyers might first bidding upwardly the price, or sellers might realize they could charge a college price. The opposite is true if the price is as well high: suppliers might be tempted to try cutting prices, while buyers might look for better deals.
- There is strong support for marketplace predictions in the evidence from experimental markets. When buyers and sellers meet individually and bargain over prices, we typically run across an upshot very similar to the marketplace outcome in Figure four.5 "Market Equilibrium".
- The supply-and-need framework generally provides reliable predictions most the movement of prices.
Pictures like Effigy four.5 "Market place Equilibrium" are useful to assistance sympathise how the market works. Continue in mind, however, that firms and households in the market do not need any of this data. This is one of the beauties of the market. All an individual firm or household needs to know is the prevailing marketplace price. All the coordination occurs through the workings of the market place.
Key Takeaways
- The primary factor influencing demand for housing is the price of housing. By the law of demand, as price decreases, the quantity of housing demanded increases. The need for housing also depends on the wealth of households, their electric current income, and involvement rates.
- The master factor influencing supply of housing is the price of housing. As price increases, the quantity supplied also increases. The supply of housing is shifted by changes in the price of inputs and changes in technology.
- The quantity and price of housing traded is determined by the equilibrium of the housing market.
Checking Your Understanding
- What would be the touch on of a decrease in the cost of borrowing on the market place supply curve of housing? What would be the impact of a decrease in the cost of borrowing on the market need curve?
- Name two events that would cause the housing market supply curve to shift rightward. Name ii events that would cause the housing market demand curve to shift rightward.
Source: https://saylordotorg.github.io/text_macroeconomics-theory-through-applications/s08-01-housing-supply-and-demand.html
Posted by: strakertwereen1972.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Are The Price And Demand For Changes In Real Estate Prices Related"
Post a Comment